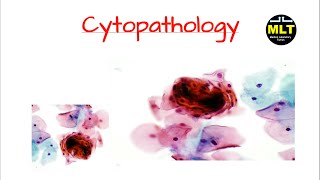
Cytology Department
Cytology also knows as cytopathology. It is a branch of pathology to diagnose a disease or other type of cancer with the help of a microscope. In which cells of the organ are studied with staining under a microscope to look for morphology or characteristics of abnormal cells. The cytology test is different from biopsy. For the cytology test with a microscope, the specimen is collected by a fine needle. The specimen is body fluid samples. The fluid is collected from the body cavities to diagnose and treatment of the disease.
Specimens are obtained from the following area to diagnose a disease.
Ascitic fluid: Ascitic is removed from the abdomen.
Cerebrospinal fluid(spinal fluid): which is obtained from the space around the brain and spinal cord.
Pericardial fluid: which is received from the sac around the heart.
Pleural fluid: which is removed from the space around the lungs.
Sputum(phlegm): which are lung secretions, mucus, collected during coughing.
Urine: which is collected by a clean-catch urine sample in a doctor's office.
Fine needle aspiration: Fine needle aspiration is a technique which comes under both biopsy or cytology test. In which the specimen (body fluid or tissue from the needle ) is removed by using a thin needle in a syringe. This process is performed by a specialized doctor. Ultrasound or computed tomography(CT) scans are used to guide the doctor to correct location
Scrape or brush cytology: A doctor also performs scrape or brushes tissue from the breathing tubes, cervix(pap test), esophagus, mouth and stomach for a cytology test.
The specimen is also obtained from the hollow region
The technique of staining to the cells and tissue is called ‘histochemical staining’ or ‘histochemistry.
Why do cytology: the doctors not only diagnose the disease but also screen the cancerous cells or non-cancerous cells. Pre-cancerous cells look like the cancerous cells but not tern into cancerous cells. Cytology test is the initial step to screening the cancer and, for conformation needs to be performed further tests. Cytology tests are always performed with a microscopy examination. Before the microscopy examination, the specimen should be stained. The staining process is necessary for microscopy examination. Stain reveals the structure of cells such as the nucleus, cytoplasm and cellular architecture and abnormalities. There are three steps to performing a cytology test. Specimen collection, techniques(procedure, preparation of smear, fixation and cytological staining).
Microscopic evolution of smear. Papanicalou(pap) is one of the most used procedures and comprises of several synthetic dyes. Papanicolaou stain ia recommended for staining alcohol-fixed cytology slides. Romanowsky stains are usually employed on air-dried smears, but they can also be utilized on wet fixed slides.Hematoxylin, a common nuclear stain, and OG-6(Orange G) and EA (Eosin Azure), two cytoplasmic counterstains, are used in the Papanicolaou staining process. This technique produces clear nuclear detail and cytoplasmic transparency, enabling the examiner to see the cellular morphology with clarity. For nuclear staining, a progressive or regression approach might be applied. There are numerous automatic programmed stainers available. Romanowsky stain is used for air-dried stains. Romanowsky stains are combinations of eosin and methylene blue, works by producing azure colors through the demethylation of thiazines and the acidic component of eosin. They are metachromatic, in contrast to the Papanicolaou stain. Unlike the methyl alcohol-based Romanowsky stains used in hematology, the majority of cytology's use of these stains are aqueous.
Pap stains are used regularly in the laboratory for cytology tests. The following steps involved in the test performance:
Fixation: the specimen smear is fixed in 95% ethyl alcohol or for other substitutes, keep it for 15 minutes.
Staining: the objective of staining is to define or differentiate the cellular structure
Nuclear staining: nuclear is stain by the hematoxylin, that is modified form is used in the papanicolau staining. In which the excessive hematoxylin are removed by alcohol(40%ethyl alcohol) or 0.05% aqueous solutionHCL alone.
Cytoplasmic stain: OG-6(monochrome) and EA-36(polycrome stain)
Dehydration: Absolute alcohol(ethanol, isopropanol and denature alcohol) is use to dehydrate the smear slide(rinse).
Clearing: After the above step, xylene can be applied on the smear. Xylene replaces alcohol
Slide mounting: After the all process, the slide is cover slipped with mountant that protect it from drying, oxidation and stain fading.
Reference:
1.https://www.cancercenter.com/diagnosing-cancer/diagnostic-procedures/cytology-tests
2.https://www.msdvetmanual.com/clinical-pathology-and-procedures/diagnostic-procedures-for-the-private-practice-laboratory/cytology
3. https://librepathology.org/wiki/Cytopathology
0 comments