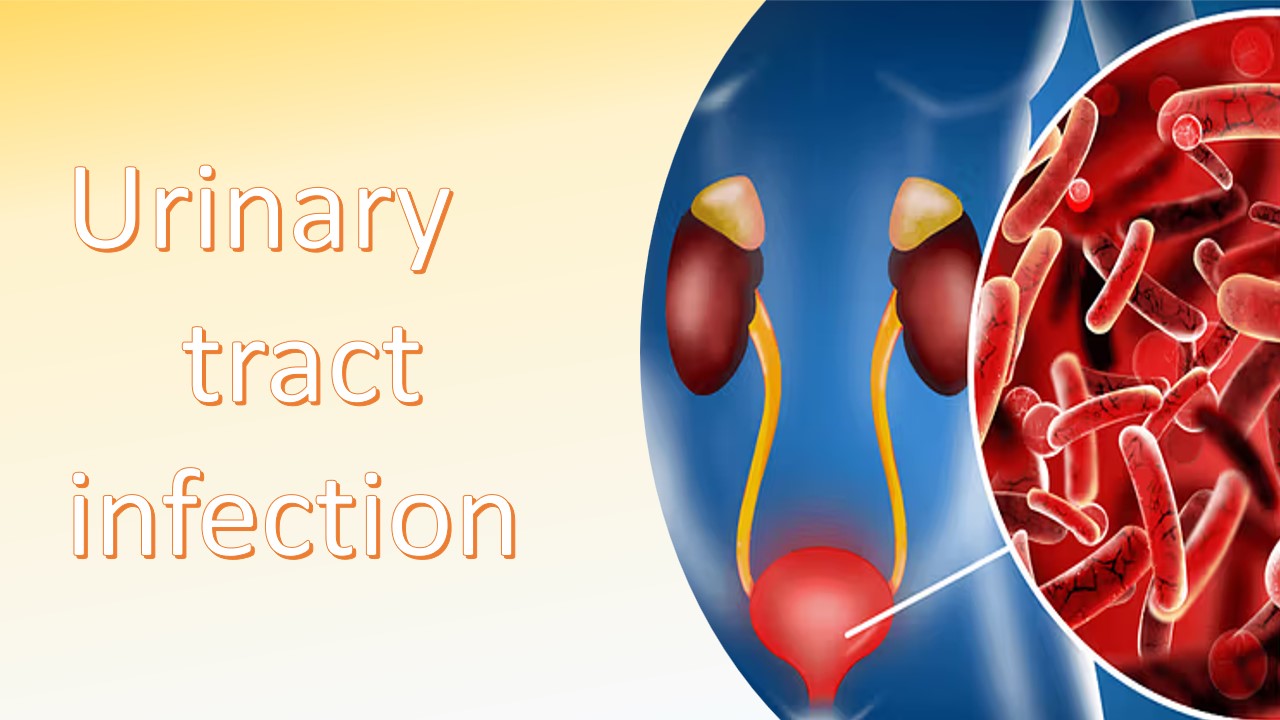
Urinary tract infection
Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are infections that occur in any part of the urinary system, which includes the kidneys, bladder, ureters, and urethra. These infections are typically caused by bacteria but can also be caused by viruses or fungi. The most common causative agent for UTIs is bacteria, and Escherichia coli (E. coli) is the predominant pathogen responsible for the majority of cases. The upper and lower urinary tracts make up the urinary system. The lower urinary tract is made up of the bladder and urethra, and the upper urinary tract is made up of the kidneys and ureters.
There are three types of UTI, depending on which areas of the urinary tract that might get infected. Every type has a unique name that corresponds to its location. Such as Bladder cystitis: It is an infection of the bladder . It is caused by a blood born bacteria. In which symptoms like frequent and painful urination, urgency, and lower abdominal discomfort.
Pyelonephritis (kidney inflammation): Infection of the kidneys. This condition can result in fever, chills, nausea, vomiting, and side or upper back pain.
Urethritis: This condition affects the urethra and can result in burning and discharge.
Symptoms
- Pain or burning while urinating
- Frequent urination
- Feeling the need to urinate despite having an empty bladder
- Bloody urine
- Pressure or cramping in the groin or lower abdomen
- Cloudy, dark, bloody, or strange-smelling pee
- Feeling tired or shaky
- pain in the back and sides
- chills and shivering
- Nausea and vomiting
Causes/Risk factors
- Kidney infection
- Previous UTI
- Pregnancy
- Age
- Poor hygiene
- Sexual activity
- Changes in the bacteria that live inside the vagina, or vaginal flora.
- Escherichia coli
- Protus mirabilis
- Enterococcus faecalis
- Staphylococcus saprophyticus
- Klebsiella pneumoniae
- Diabetes
Diagnosis
Urinalysis tests along with microscopy examination are used to diagnose the which type of bacteria that cause the urinary tract infection. For the identification of the bacteria, Gram staining are used. Wright’s stain and Sudan III stain both are also use to find out blood and biological particles(lipid) in urine. After the microscopy examination the white blood cells(WBC) and bacteria around the cells are observed in bacilli form.
Bacilli (rod-shaped bacteria, as black and bean-shaped) shown between white blood cells in urinary microscopy.
Reference:
1. https://simple.wikipedia.org/wiki/Urinary_tract_infection
2. https://www.cdc.gov/uti/about/index.html
0 comments