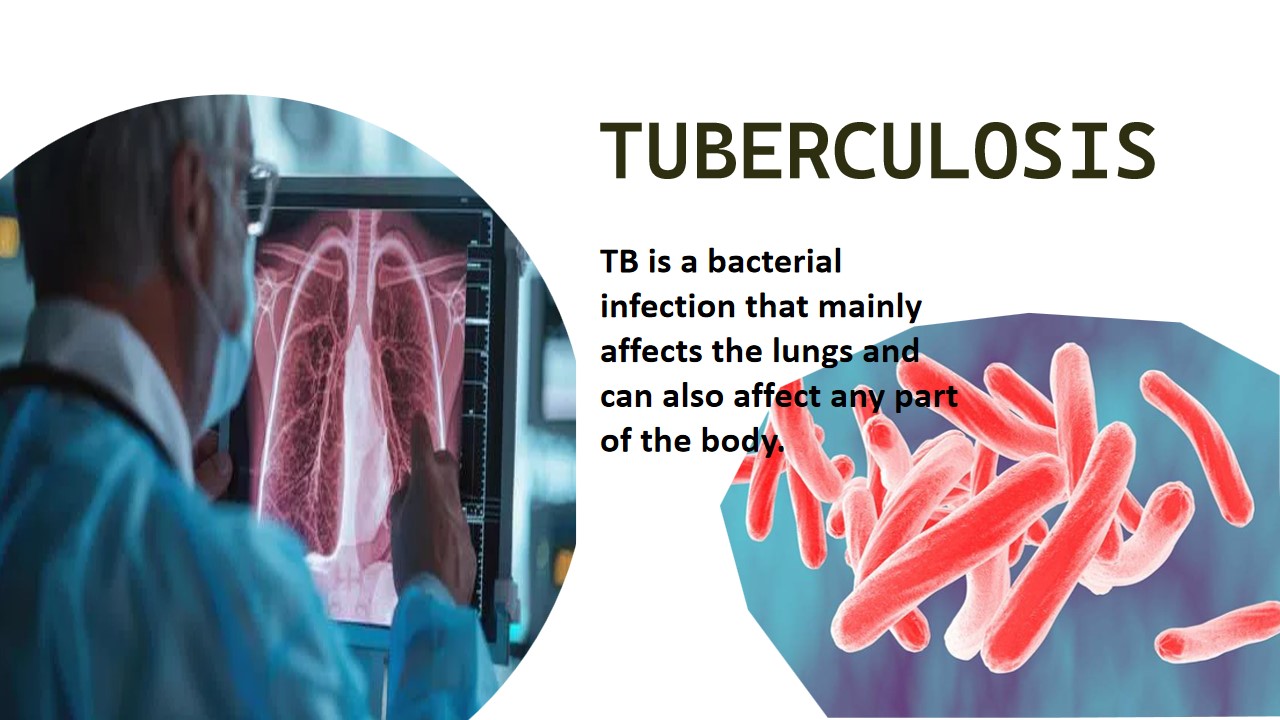
Tuberculosis
Tuberculosis(TB) is caused by a bacteria called Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Mycobacterium tuberculosis is a Gram positive, rod shaped, filamentous and acid-fast bacteria that mainly affects the lungs or other parts of the organs, including the kidney, spine, brain .Mycobacterium tuberculosis bacteria is affected to the person those who have weakened immune system(immunocompromised person), people have a family history TB, baby infected through mother during pregnancy. TB bacteria cause the disease after several months or years before the bacteria live in the body in the latent phase. In this phase, disease symptoms are systemic in this phase.
There are three stages to developing severe tuberculosis, including primary infection, latent infection and active TB disease. In the primary infection: the body's immune system fights against the bacteria. Latent infection: the causative bacteria live in the body but don’t make risk of tuberculosis. Active TB disease : in which the body's immune system becomes weakened, it does not fight with theMycobacterium tuberculosis. . which commonly attacks the lungs and harms other organs ( spleen, kidney).Tuberculosis(TB) is spreads from person to person when the infected person coughs, sneezes, talks and sings. TB is not spread by touching and sharing food or dishes.
Symptoms
- Cough
- Coughing up blood or mucus
- Chest pain
- Pain with breathing or coughing
- Fever
- Chills
- Night sweats
- Weight loss
- Not wanting to eat
- Tiredness
- Not feeling well
Cause/Risk factor
- Causative agents like Mycobacterium tuberculosis
- Smoking and using other tobacco products
- Misuse of alcohol
- HIV/AIDS
- Diabetic patient
- Severe kidney disease
- Working in health care and treating people with a high risk of TB
- Fetus from infected mother
Diagnosis
Cytology department
Cytology examination is used to detect tuberculosis along with the microscope.in which Ziehl-Neelsen stain also know as acid fast stain is use to stain the causative bacteria to observed under microscope. The Acid fast staining method is a standard diagnostic tool and gives the rapid diagnosing of tuberculosis in samples like sputum. The outer layer of bacteria (Mycobacterium tuberculosis) is covered with waxy lipid that contains with mycolic acid.
Ziehl-Neelsen stain procedure using carbon fuchin. Mycobacterium tb is an acid fast bacteria.These bacteria absorb the red or pink color and show against the blue or green background depending on counter stain used.
Ziehl-Neelsen stain is a two steps process. On first step, the sample is stain with the basic fuchsin solution. It makes the cells pink. Then, in the second step, apply the acid alcohol solution. These are decolonised all cells except for acid fast cells. After that, cells become red and observed under the microscope.
Histology department
Biopsy (removal of small tissue from the lung) specimen is used to conformation of the TB. These specimens were examined under the microscope. After obtaining the sample, it was sent to the laboratory for further process. Fixation, processing, embedding, sectioning, and sometimes antigen retrieval are performed in the laboratory.stained the microscopy slide with H and E stain and observed the slide under a microscope.
Microbiology department
Microbiological examination of TB is conformed by the sputum culture method. The growth of the M. tuberculosis is observed on the media plate. Take a colonies and spread on the glass slide and also apply gram staining and observe under the microscope.
Reference:
1.https://www.webmd.com/lung/understanding-tuberculosis-basics
2.https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/11301-tuberculosis
0 comments