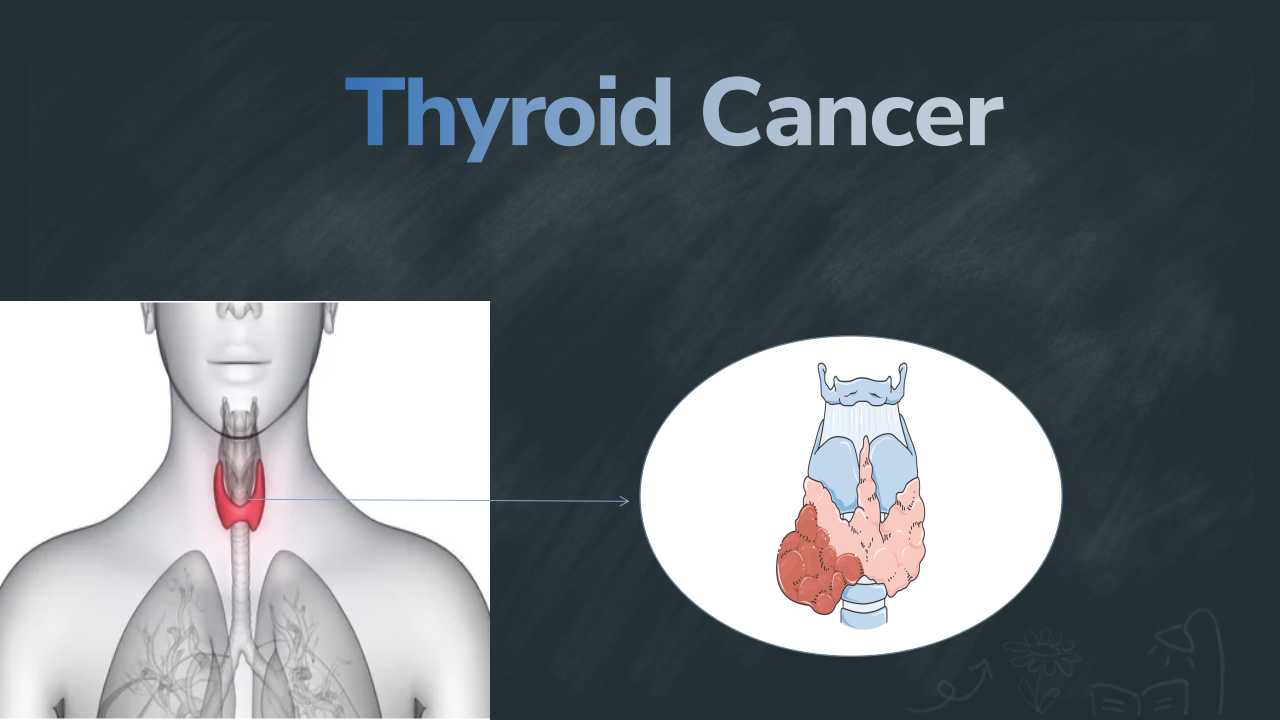
Thyroid cancer
Thyroid cancer is one of types of endocrine gland cancer. Thyroid cancer is develops in the thyroid when abnormal cells grow or multiply unnecessarily due to mutation or changes. The thyroid is an important organ of the body,which looks like a butterfly-shaped gland. Thyroids are located inside the lower front of the neck. The function of the thyroid gland is to produce hormones called thyroid hormones. Thyroid glands regulate the body's metabolism, control body temperature, blood pressure and heart rate.
There are four types of Thyroid cancer which are classified based on the types of cells from which cancer grows.
Papillary: about 80% of thyroid cancer cases is papillary thyroid. papillary cancer,This type of cancer mainly spreads to lymph nodes in the neck
Follicilar: Follicular cancer spreads to bones and lungs. This type of cancer is difficult to cure because it is categorized as metastatic cancer.
Medullary: Medullary cancer is found in rare cases. This type of cancer develops if a patient has a family history of the disease or thyroid cancer.
Anaplastic: Anaplastic cancer is a dangerous cancer because it quickly spreads into surrounding tissue and other parts of the tissue. Anaplastic thyroid cancer is harder to cure.
Symptoms
- Difficulty in breathing
- swallowing
- Loss of voice (hoarseness).
- Swollen lymph nodes in your neck.
- Tiredness
- Loss of appetite
- Nausea and vomiting
- Unexpected weight loss
Cause/Risk factor
- Enlarged thyroid (goiter)
- Family history of thyroid disease or thyroid cancer
- Thyroiditis (inflammation of your thyroid gland)
- Gene mutations (changes) that cause endocrine diseases, such as multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2A (MEN2A) or type 2B (MEN2B) syndrome.
- Obesity
Diagnosis
Cytology examination:Using a tiny needle, FNA biopsy involves removing cells from thyroid tumors or nodules. Usually, ultrasonography is used to guide this treatment so that it targets particular regions of the thyroid gland. A pathologist or cytologist will next put the harvested cells onto slides, color them, and inspect them under a microscope.
Histology department: thyroid cancer is diagnosed by a cytology test. The specimen is aspirated from the thyroid nodule, It is called the fine needle aspiration cytology(FNAC). The smear is fixed on the glass slide and applied the modified papanicolaou stain. Other stains, such as Romanovsky stain , are also used in thyroid cytology.After performing the staining process, the smear slide was examined under the microscope. Fine needle aspiration cytology(FNAC) along with the microscopy examination show the microfollicular structure and crowded cellular clusters.
Diagnosis of Papillary Thyroid Cancer Uniform nuclei and pale cytoplasm by papanicolaou stain method under a microscope
References-
1.https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/12210-thyroid-cancer
2.https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK285544
0 comments