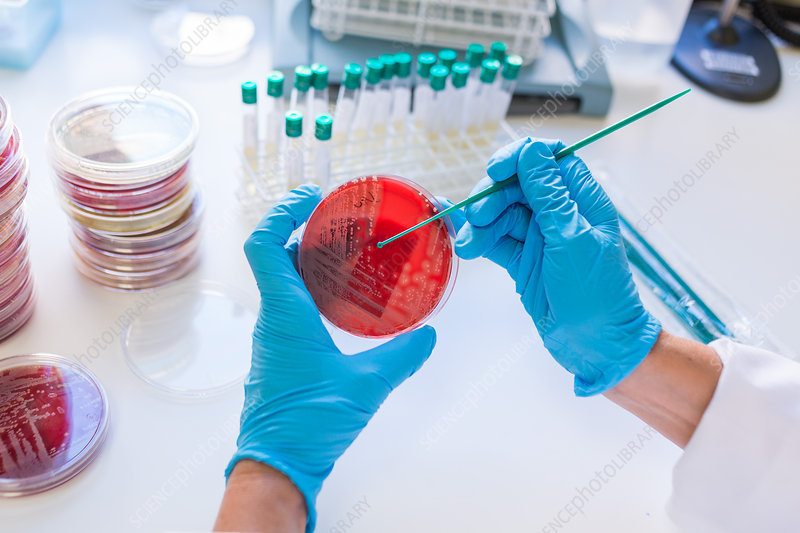
Microbiology
Microorganisms are too small or tiny organisms present in the environment but can’t be visible by the naked eye and the study of microbes is called Microbiology. Microorganism including bacteria, archaea, viruses, fungi, prions, protozoa and algae, knows as microbes. These microbes play a vital role in the environmental process, including the nutrient cycle, bio-degradation or deterioration, climate change, food spoilage.But these microbe helps to human being by several ways such as to develop drug, biofuel, acts as pollution cleanser, used in beverage and food industry and many other purpose in industry. But some microbes are threatens or dangerous to health.
In the field of medical science, the microbiologist (microbiologist is a doctor or pathologist who has expert or specialized in microbiology) discovers new things that are concerned about prevention, diagnosis and treatment of infectious diseases. The Medical microbiology lab (is a multidisciplinary department, to studies the microbes and diagnoses the causative agent that causes the disease). study of the microbes by microbiologists contributed to great revolutionary changes in the field of medicine or life saving processes. The microbiologist such as flaming discover the penicillin, Jenner and his vaccine against small pox, Zur Hausen who identified link between papiloma virus and cervical cancer.
Department of microbiology is composed of Bacteriology, virology, mycology, serology, HIV Laboratory, parasitology and mycobacteriology.The microbiology department offers services like automated detection, identification and antimicrobial susceptibility test (AST) by Bectec and VITEK 2, MGIT(BSL-3), LPA and Gene Xpert for routine diagnosis of TB ,department also provides facility of fluorescent microscope. The microbiology laboratories are equipped with the latest equipment that provide reliable testing results. Light microscope, incubator,oven, Autoclave, fridge and refrigerator, safety cabinet, electronic balance, pH meter, Hot-plate, micro-pipette, Water bath, Distillator, Flasks, beakers, petri-dishes, loops, Magnetic stirrer, Spectrophotometer, High Performance Liquid Chromatography(HPLC), Gas chromatography(GC), Gel Elecrophoresis, VITEK, BacT/ALERT 3D system, Polymerase chain reaction(PCR) technique. A microscope is an important equipment because a tiny or too small object can be seen through it, that object is not seen by the naked eye. Ocular lens, objective lens, arm, stage, stage clips, coarse adjustment knob, fine adjustment knob, light source, condenser and base. Ocular lens with constant magnification (10X), Objective lenses could be(4X,10X.40X,100X).
The samples are used in the microbiology department, include blood, bone marrow, CFS, pus, bile, urine, respiratory sample(sputum, BAL, ET aspirate, Lung aspirate), sterile body fluid, Faecal specimen, catheter, tips of central lines, throat and nasal swabs, other swab, Drain, aspirate, biopsy, Cervical discharge, Urethral, discharge, semen these are use for diagnosis of disease.
The staining technique is a crucial process for the identification of microorganisms coupled with microscopy examination, in which stain or dye is used to increase the visibility of a biological specimen under a microscope. Staining technique gives information about the cell’s structure, integrity, differentiates between different cell types, and improves the contracts and gives more details about cells ' margins. In microbiology laboratories, there are various types of stains are used, each stain is designed for specific cellular organelles or cellular components. Some common stains used are basic stain (methylene blue, crystal violet) and acidic dye (eosin, acidic fuchsin).
The Staining process involves the following steps:
- Fixation: The smeared glass slides are preserved by fixative, like formaldehyde or alcohol, that prevents the smeared glass slide from decaying and maintains cellular integrity.
- Permeabilization: some stains require permeabilization to penetrate in the cell membrane. This step ensures that the stain reaches the internal structure.
- Staining: The most popular stain is Gram staining, Acid fast satin, Zeel Nesel staining, and other staining are also used in the laboratories.
- Washing: Washing is the final step in which an excessive amount of stain can be removed by maintaining cell integrity and providing a clear image.
After the staining process, the smear slide ready to be observed under a microscope. Microscopes give accurate information about the causative agent of disease and also differentiate cell types. The staining process, coupled with microscopy, is a fundamental technique that helps researchers and scientists to visualize and analyze cellular structures and discover new approaches in the field of medicine, research and pathology.
Reference:
1.https://us.vwr.com/store/category/hematology-stains/3617555
2.https://bio.libretexts.org/Learning_Objects/Laboratory_Experiments/Microbiology
_Labs/Microbiology_Labs_I/12%3A_Oral_Biofilms
3.https://www.upums.ac.in/StaticPages/MicrobiologyDepartment.aspx
4.https://www.slideshare.net/HusseinAltameemi2/medical-microbiology-laboratory-introduction-terminology
0 comments