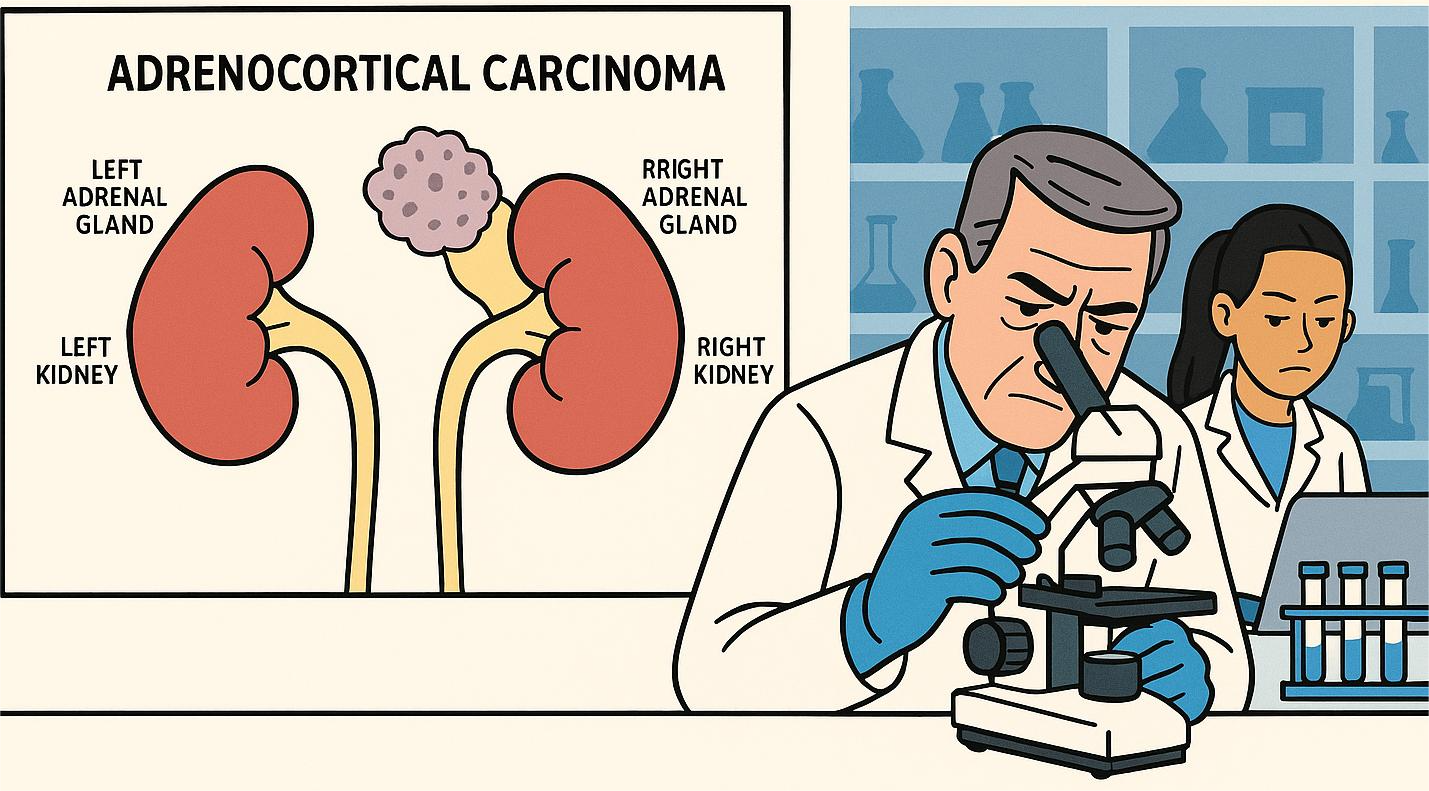
Adrenal cancer
Neuroendocrine tumors (NETs) are a class of cancers that includes adrenal cancer. These can originate in any of the body's hormone-producing glands. The adrenal glands are tiny glands where adrenal cancer first appears. Each kidney has one adrenal gland which is situated on top of the kidney. Either one or both may get cancer. Hormones are molecules produced by the adrenal glands that assist in regulating body functions. They have an impact on blood pressure, hair growth, and even stress management. Numerous adrenal tumors produce their own hormones. The cortex is the outer layer of adrenal glands, is the possible site of a tumor. A tumor that develops in the medulla, the central region, may possibly be the initial cause of the sickness.
Malignant refers to cancerous adrenal tumors. Benign ones are those that are not cancer. Tumors that are malignant include, cortex, or outer layer, of the adrenal gland, where adrenal cortical carcinoma first appears. Since the majority of these tumors are active, they produce hormones.The middle, or medulla, is where malignant adrenal pheochromocytoma first appears. It is extremely uncommon. In children, neuroblastoma also starts in the medulla. Adrenal gland may develop an internal or external malignant paraganglioma. Benign tumors include, Adenoma, which produces more cortisol, leading to the condition called Cushing’s syndrome. Other tumor such as Benign pheochromocytoma and paraganglioma.
Symptoms
- Weight gain
- A puffy face
- Fine hair on face, upper back, or arms
- Stretch marks
- Weaker bones and muscles
- Easy bruising
- Mood swings
- Depression
- High blood pressure
- High blood sugar
Cauces/Risk factors
- Li-Fraumeni syndrome
- Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome
- Carney complex
- Multiple endocrine neoplasia
- Familial adenomatous polyposis
- Lynch syndrome
Diagnosis
Histology Department
Histological examination of adrenal cancer involves the microscopic analysis of tissue samples obtained from the adrenal glands. The specimen is obtained from the patient by using the biopsy (remove small tissue) and sent to the laboratory for the histological examination. Firstly, perform the gross examination and then apply stains, mostly H&E stain . The histological examination plays a crucial role in confirming the diagnosis, determining the tumor grade, and guiding treatment decisions.
Histological examination of adrenal cancer
Reference:
- https://www.webmd.com/cancer/adrenal-cancer
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Adrenal_tumor
0 comments